Georgia, Inland Waterways, National Category
Startup Uses Drone for Cleaning Water, Collecting Data


The U.S. rail network consists of approximately 140,000 miles of track and serves freight and passenger services. Freight rail supports the movement of 1.5 billion tons of goods annually. Amtrak reported 28.6 million passengers in 2023, up from 22 million in 2022. Ridership on the Northeast Corridor shows fast growth, with passenger services on the national network increasing in frequency, speed, and scope. The Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) authorized $66 billion for rail projects from Fiscal Year 2022 to 2026, making vital improvements such as intercity passenger rail service expansion, Amtrak corridor development, and road–rail crossing grade separation possible. Train safety incidents show a promising long-term trend, down 23% in the 23 years from 2000 to 2023, but recent incidents like 2023’s derailment in East Palestine, Ohio, raise concerns and is just one of 10,577 incidents that year. Recent programs and actions implemented by the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) can improve the rail network, which calls for a balance between modern advancements in the sector, such as precision-scheduled railroading, and sufficient staffing to ensure public safety.
increased by nearly 40%
between 2000 and 2022
includes $66 billion in rail infrastructure funding
over 5 years
in project upgrades achieves $4 in cost savings that would have been spent
to address failures

Freight rail companies own and maintain their own infrastructure, while U.S. passenger rail consists of Amtrak and commuter rail systems that transport riders from suburban communities to dense urban centers.
Freight rail companies in the U.S. invest an average of 18.4% ($23 billion) of their revenue on capital expenditures annually. Class I railroads do not report an unfunded need or deferred maintenance. Short line railroads specifically invest 25% of their annual revenue in Operation and Maintenance.

Competing interests between freight and passenger rail unfortunately continues to pose ongoing operational challenges. For 2023, Amtrak reports issues with on-time performance (OTP), showing an overall 74.4% OTP for customers. Federal law requires freight railroad dispatching to prioritize Amtrak trains over freight, but the agency contends this is often ignored and results in lower OTP. Freight and passenger rail can benefit from partnerships to improve track sharing and avoid delays such as the Chicago Region Environmental and Transportation Efficiency Program.

Freight railroads have experienced improved safety over the last two decades, although an uptick of incidents has been reported in recent years. For Class I railroad employees, fatality and injury rates for freight rail employees have dropped 63% since 2000, reaching an all-time low in 2023. However, more incidents and fatalities have been reported recently. According to Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) safety data, railroad deaths totaled 970 in 2023, an 7% increase from 2022’s 904 and much higher than nearly a decade ago. Overall incidents were 10,578 in 2023, also larger than immediately preceding years. Overall incidents were 10,551 in 2023, also larger than immediately preceding years. Trespassing is the top cause of rail-related deaths with a high number of incidents also occurring at highway-rail grade crossings.
Rail lines face considerable threats from extreme weather, making resilience a key priority for future projects. In 2024 alone, Hurricane Helene damaged to rail lines in the Southeast, while rising waters caused the collapse of a rail bridge over the Big Sioux River between South Dakota and Iowa, and excessive heat along the Northeast Corridor delayed Amtrak trains due to fires and speed restrictions.
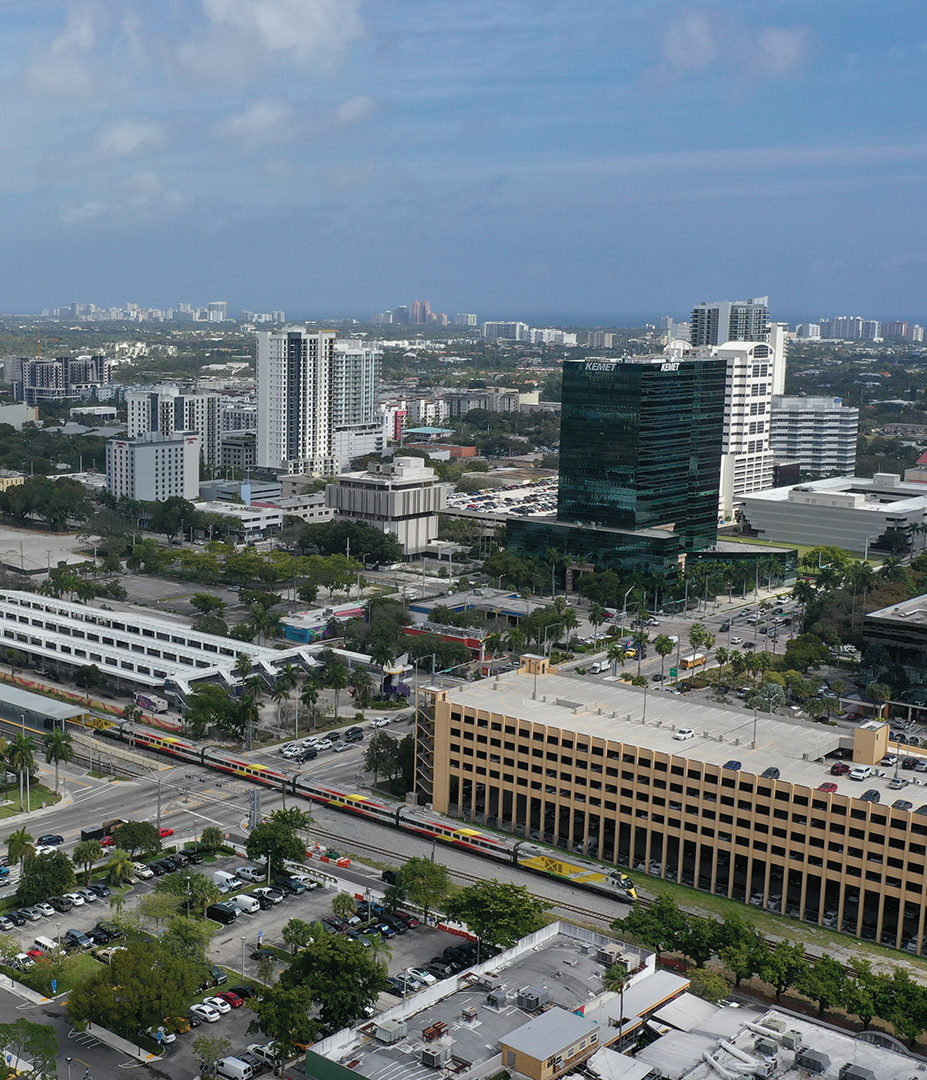

Photo Attributions
Select your home state, and we'll let you know about upcoming legislation.
"*" indicates required fields